Mesothelioma Cells & Types
Learning more about the origin of your cancer and its cell type will help you better understand your prognosis and treatment options. The cancer’s location and cell type could impact your treatment and survival.
How Does the Type of Mesothelioma Impact Treatment?
There are different types of mesothelioma cells and different places where mesothelioma develops, accentuating the importance of an accurate diagnosis and a personalized approach to treatment.
No two cases are exactly alike, and neither should they be treated the same way.
A mesothelioma cancer prognosis can vary greatly, depending on a number of factors, including where the cancer was found and the cellular makeup of the cancer. This is a rare and fast-growing cancer, making it vital to find a specialty center with experience in identifying it correctly, and treating it accordingly.
Specific cell types have different visible characteristics. They behave differently, too, responding to therapies in unique ways. The same goes for the cancer’s location. Different treatments are recommended depending on where the cancer originally formed. Doctors will consider the cancer’s location and cell type to develop a treatment approach to give you the best possible odds of surviving.

Types of Mesothelioma
Pleural mesothelioma accounts for an estimated 75 percent of all cases. It develops first in the pleura, the thin lining around the lungs. The prognosis is typically poor and survival averages around one year, although a good specialist and recent treatment advances provide hope to survive longer than average. It can take anywhere from 20 to 50 years for asbestos to damage cells and DNA enough to cause mesothelioma. But once diagnosed, it often moves quickly and is difficult to control.
Peritoneal mesothelioma accounts for an estimated 20 to 25 percent of cases and develops first in the peritoneum, a thin layer of tissue that covers the abdominal organs. Although there is no cure, peritoneal patients who receive treatment typically survive longer than pleural mesothelioma patients. Early symptoms that often lead to a diagnosis include abdominal pain, abdominal swelling, fatigue and weight loss. Patients have experienced longer survival recently with the hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) procedure immediately following surgery.
Both types account for 1 to 2 percent of all mesothelioma cases. Pericardial mesothelioma develops in the thin membrane surrounding the heart. Testicular mesothelioma involves the membrane that covers the testicles, and those diagnosed often have no history of asbestos exposure. Patients with testicular mesothelioma have survived considerably longer than those with other types of mesothelioma.
Mesothelioma Cell Types
Doctors typically develop a treatment plan and provide a prognosis based upon the cell type — sarcomatoid, epithelial or biphasic — but differentiating between them can be difficult because the characteristics are so subtle. The cell type will indicate how aggressive the cancer is, and what the treatment should be. There is considerable difference in life expectancy of a patient based upon the cell type, more than 200 days according to clinical data.
- Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
-
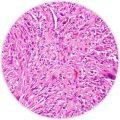
Sarcomatoid is the most aggressive mesothelioma cell type, often eliminating major surgery as a potential option because it will have little effect on survival. Sarcomatoid cells are the most resistant to therapy.
It is the least common of the three major types, accounting for 10 to 20 percent of the pleural mesothelioma cases and less than 5 percent of the peritoneal cases. The cells appear spindle-shaped and elongated, often forming tumors with a fibrous pattern.
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma may be misdiagnosed as other less serious illnesses, mistaken for pleural liposarcoma, fibrous pleurisy or even just localized fibrous tumors. Pathologists need a sizeable tissue biopsy to make a correct diagnosis.
- Epithelial Mesothelioma
-
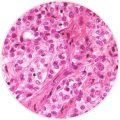
Epithelial cell type responds best to treatment and accounts for 50 to 70 percent of the cases. Most of the research focuses on this cell type, giving doctors a better understanding of its behavior. It most commonly occurs in pleural mesothelioma.
Mesothelioma epithelial tumors are sometimes misdiagnosed as adenocarcinoma, which develops in the lungs and breast. It often takes a thoracoscopic biopsy to accurately diagnosis this cell type. The cells are sharply defined and uniform, often with complex, branching patterns.
- Biphasic Mesothelioma
-

Biphasic is the classification given when both epithelial and sarcomatoid cells are present. An estimated 25 to 30 percent of cases are classified as biphasic. The prognosis often depends on what percentage of the cells is epithelial. The higher the percentage of epithelial cells the better the prognosis.
This type also is more common among pleural mesothelioma patients than peritoneal. The different cell types are often in distinctly separate areas of the mesothelioma tumors.
Diagnosing Mesothelioma
There is no clear path to a mesothelioma diagnosis. It can be a long and winding road that includes blood tests, imaging tests and multiple biopsies. The characteristics of the particular cell types are very subtle, which can make a proper diagnosis quite challenging. Early symptoms of mesothelioma are often confused with those of more common and less-serious illnesses.
It can take a team of doctors, including an experienced pathologist and oncologist, who know the subtleties to identify the disease. It is important for a patient to notify the medical staff if they have a history of asbestos exposure, which is the primary cause of the disease.
Even after a diagnosis, it is important for a patient to find a specialty center and an experienced doctor. Patients too often rely on an oncologist without experience in mesothelioma and are told there are no options beyond chemotherapy. Recent advancements make almost everyone treatable in some way.

Surviving Mesothelioma
The epithelial cell type will give patients a better chance of long-term survival. And despite all the gloom and doom you may read on the Web, it is not unusual for patients who elect treatment to survive three years and beyond. Progress is mounting in the treatment and management of mesothelioma. There are some survivors who have lived 10 years after a diagnosis. Why not try to be one of them? It’s important to know they are out there.
The best chance of long-term survival is with epithelial mesothelioma, particularly if it is diagnosed early in the growth process, before it has had a chance to spread (metastasize). Many of the long-term survivors attribute their success to good fortune and finding a doctor who is familiar with this rare cancer.
 Do You or a Loved One Have Mesothelioma?
Do You or a Loved One Have Mesothelioma?